The Best Visual Composer Alternatives to Pick From
June 12, 2024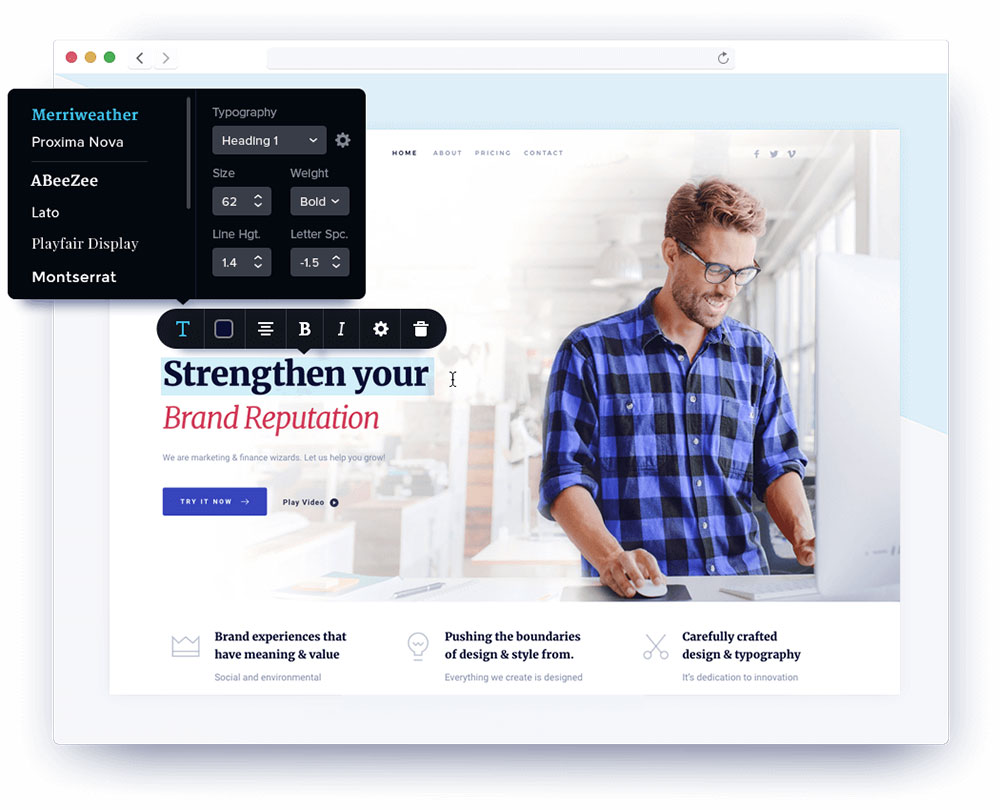
13 WooCommerce Page Builders You Need
June 15, 2024The world of web design is an ever-evolving landscape where creativity meets technology. Every pixel you place and every line of code you write shapes the digital experiences that can captivate audiences.
Mastering web designer skills isn’t just about knowing HTML/CSS or being proficient with Adobe Creative Suite; it’s about understanding the nuances of UX/UI design, creating responsive layouts, and implementing effective SEO fundamentals.
But what truly distinguishes an exceptional web designer? Do you know how typography influences user experience or how wireframing can streamline design projects?
Whether you’re familiar with JavaScript basics or harness the power of CMS platforms like WordPress, this guide will unveil everything you need.
By the end, you’ll gain deep insights into responsive design, cross-browser compatibility, and so much more. Discover how principles of color theory, user-centered design, and web accessibility can transform your projects.
Web Designer Skills
| Skill Category | Skill | Description | Importance Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical Skills | HTML/CSS | Fundamental building blocks for creating and styling websites. | High |
| JavaScript | Adds interactivity and dynamic content to web pages. | High | |
| Responsive Design | Ensures websites function well on all devices, including mobiles and tablets. | High | |
| UX/UI Design | Focuses on user experience and interface design for intuitive and attractive websites. | High | |
| Graphic Design | Creates visual content and layouts for web pages. | Medium | |
| SEO (Search Engine Optimization) | Enhances website visibility in search engines. | Medium | |
| Version Control (Git) | Manages code changes and collaboration with other developers. | Medium | |
| Creative Skills | Creativity | Ability to generate original ideas and innovative designs. | High |
| Typography | Understanding of fonts and text layouts to enhance readability and aesthetics. | Medium | |
| Color Theory | Knowledge of color schemes and their impact on user perception and behavior. | Medium | |
| Analytical Skills | Problem-Solving | Identifying issues and developing effective solutions. | High |
| Attention to Detail | Ensuring precision in design elements and code. | High | |
| Communication Skills | Client Communication | Effectively understanding and responding to client needs and feedback. | High |
| Team Collaboration | Working well with other designers, developers, and stakeholders. | Medium | |
| Project Management | Time Management | Prioritizing tasks and managing time efficiently to meet deadlines. | High |
| Project Planning | Planning and executing project phases and deliverables. | Medium |
Core Technical Skills
HTML & CSS
Importance of HTML and CSS in Web Design
When it comes to building a website, having a solid grasp of HTML and CSS is crucial. These are the foundational blocks of any webpage.
HTML provides the structure, while CSS adds the stylistic flourishes. Imagine HTML as the skeleton—it gives shape and form.
CSS, on the other hand, is the skin, hair, and clothes, making everything look aesthetically pleasing. Together, they create the spine of web design.
Key Concepts and Best Practices
Diving into HTML, elements like <div>, <span>, and <p> are your bread and butter. Always stick to semantic HTML where you can.
Elements like <header>, <footer>, and <section> help define the structure clearly. In CSS, mastering the box model is essential. Margins, paddings, borders—these are the building blocks for creating layouts.
Use selectors wisely.
.class, #id, and element selectors should be used thoughtfully to ensure clean and maintainable code.
Tools and Resources for Learning HTML and CSS
The internet is brimming with tools and resources. W3Schools and MDN (Mozilla Developer Network) are two fantastic repositories for HTML and CSS tutorials.
CodePen is another great platform, not just for practicing but for seeing what others in the community are up to.
Experiment. Break things.
JavaScript and PHP
Role of JavaScript in Interactive Web Design
JavaScript is like the magic wand that brings websites to life. Whether it’s a dropdown menu, a photo carousel, or a dynamic form, JavaScript is the key. It’s not merely about making things move; it’s about enhancing user interaction and experience.
Basic to Advanced JavaScript Techniques
Start with the basics: understanding variables, loops, and functions.
Moving onto DOM manipulation—how you can change HTML and CSS with JavaScript. Once you’re comfortable, dive into asynchronous programming with Promises and Async/Await.
Frameworks like React or Vue can skyrocket your capabilities but don’t rush into them. First, solidify your vanilla JavaScript skills.
PHP for Backend Development
PHP isn’t as glamorous as JavaScript, but it’s a workhorse for backend development.
Think user authentication, form handling, or managing a database. PHP is widely supported and powers a significant portion of the web.
The beauty? PHP scripts run on the server-side, making your web applications more robust and secure.
Web Server Management
Setting Up and Configuring Web Servers
When setting up a web server, you’re setting the stage for everything that’s to come. Apache and Nginx are the go-to choices.
Configuring these servers involves setting up server blocks for different sites, enabling necessary modules, and ensuring everything is secure.
Ensuring Website Accessibility and Functionality
Ever visited a site only to find a 404 page? Proper server management ensures that your site is always accessible.
Routine checks, uptime monitoring, and load balancing are key practices.
Functional continuity is paramount.
Server software updates, SSL certificates, and database backups—maintenance isn’t just a task; it’s a ritual.
Maintenance and Security Best Practices
Regular updates and patch management are your first line of defense. Keeping your server and software up-to-date is crucial.
Firewall settings, DDoS protection, and regular security audits are not optional—they’re essential.
Always, always keep backups.
Content Management Systems (CMS)
Overview of Popular CMS Platforms
WordPress, the CMS that Be Theme is using
WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal—these names should ring a bell. A CMS simplifies the web design process, enabling you to focus more on content rather than code.
WordPress leads the pack, but Joomla and Drupal offer their unique advantages depending on your needs.
Key Features and Benefits
CMS platforms offer a plethora of features: easy content editing, extendable via plugins or modules, and a user-friendly interface.
Imagine dragging and dropping complex elements into a site without writing a single line of code.
Empowerment through simplicity.
How to Effectively Manage Content
Effective content management isn’t just about adding posts or pages. It’s about categorizing content appropriately, optimizing it for SEO, and ensuring it’s accessible.
Regular updates and utilizing well-coded plugins can keep your CMS-run site swift and efficient.
Explore and leverage the vast libraries of themes and plugins to optimize and customize.
Design Principles and Techniques
Visual Design
Fundamental Concepts: Layout, Color, Typography
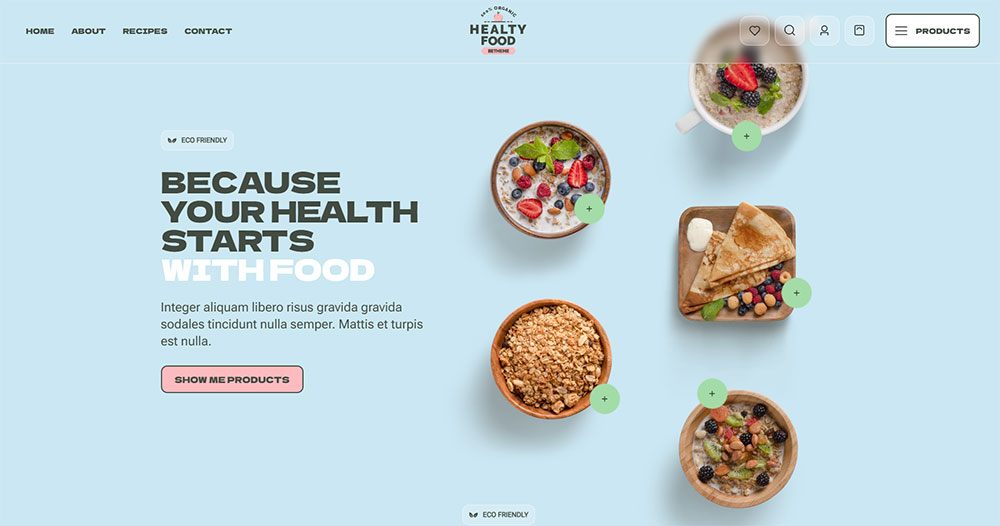
Get BeTheme and use this template
Alright, let’s get the creative juices flowing. The essence of visual design starts with three significant pillars: layout, color, and typography.
Layout is your framework—think grids and whitespace, how elements are distributed. It’s the blueprint of aesthetics.
Color? It’s the mood setter. Energetic reds, calm blues. Understanding color theory helps craft harmonious visuals.
Pair complementary colors to dazzle, or analogous colors for subtle depth. But never underestimate the power of a good monochrome scheme.
Typography, the voice of your design. Serif vs. sans-serif, the choice sets the tone. Alignment, line height, letter spacing—precision is key.
Your typeface selection isn’t just about readability; it’s about personality.
Tools for Creating Visual Designs
Onto the fun part: tools! Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, Figma, Sketch.
These are your paintbrushes.
Photoshop for intricate visuals, Illustrator for vector art, Figma and Sketch for collaborative design. Each tool has its forte.
But don’t stop there. New tools like Affinity Designer or Procreate might surprise you with their robust features.
Explore, experiment, and expand your toolkit.
Examples of Effective Visual Design
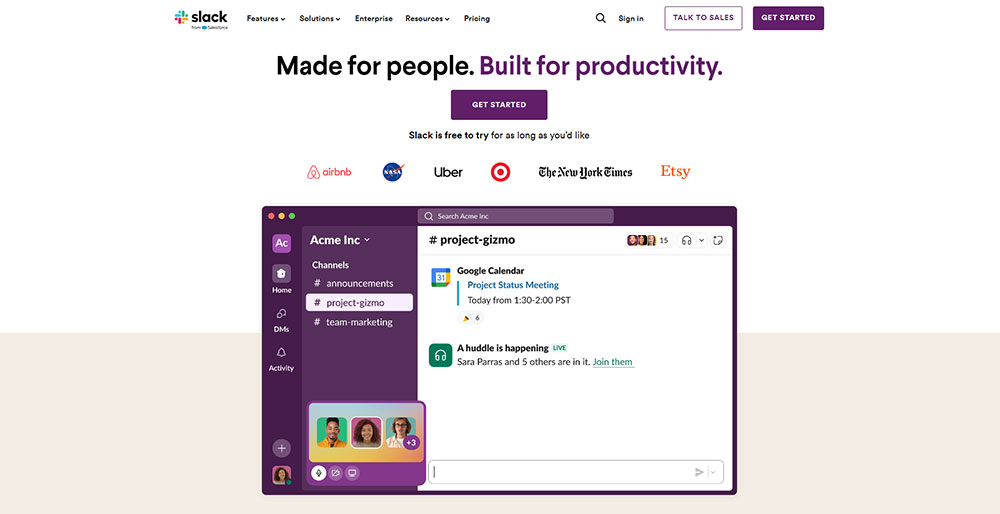
Visual storytelling is everywhere. Look at Airbnb’s clean interface, the harmonious color palette of Slack, or the typography of Apple’s website. Studying these examples offers insight.
Check out Dribbble and Behance. These platforms brim with gems showcasing excellent visual design. These are your virtual museums. Spend time in them.
UI (User Interface) Design
The Importance of UI in Web Design
UI is the handshake between user and product. It’s the first impression.
It’s not just about looking good; it’s about being intuitive. A great user interface makes interaction seamless.
Buttons click, menus drop, icons guide—all with precision.
Elements of UI: Buttons, Menus, Icons
Buttons should be assertive but not aggressive. Look at the size, color, and font. Menus? The gateway to navigation. Dropdowns, sidebars. Easy access is the mantra.
Icons are the universal language—tiny symbols bridging gaps in understanding. Think of them as the salt and pepper of your interface. Essential yet subtle.
Best Practices for Creating User-Friendly Interfaces
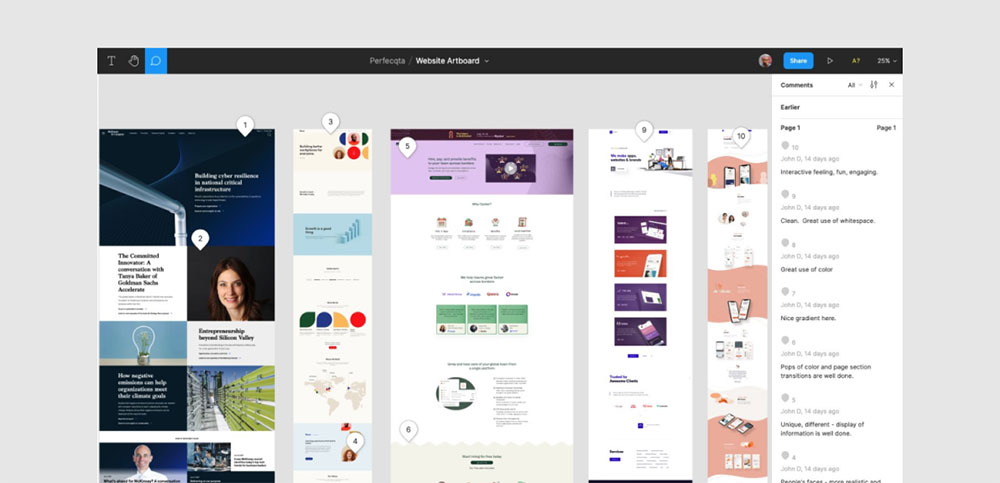
Consistency is your friend, but don’t fall into monotony. Create a cohesive design language. Users shouldn’t have to think twice. Accessibility—text for icons, alt tags for images.
Always test. Components might look stellar but falter in real-world use. Collect feedback, iterate. Tools like Figma are excellent for prototyping and user testing.
UX (User Experience) Design
Understanding User Needs and Behavior
A website without considering the user’s journey is like a ship lost at sea. Understand the user’s pain points and motivations.
Research, surveys, user interviews. Walk in their shoes. Empathy is crucial.
Designing for Optimal User Experience
Simplify complexity. Think onboarding flows, error messages, and navigation paths. User-centered design is your mantra.
Map out the user journey with wireframing tools like Balsamiq or Sketch. Blueprinting every interaction, predicting their expectations.
Usability and Accessibility Considerations
Usability ensures efficiency and satisfaction. Can users complete tasks without frustration? Accessibility broadens reach—color contrast for visibility, alternate texts, keyboard navigation. Designing with inclusivity amplifies impact.
Responsive Design
Principles of Responsive Web Design
Flexibility is essential. Websites must adapt across devices. Start with a fluid grid system. Utilize media queries to adjust layouts based on device characteristics.
Mobile-first? It’s not just a buzzword. It’s a strategy. Designing for the smallest screen first ensures essential content shines.
Techniques for Ensuring Compatibility Across Devices
Flexbox and Grid Layouts—these CSS techniques are lifesavers. They provide dynamic structuring, enabling elements to resize, reposition fluidly. Use images wisely; responsive images with srcset and <picture> tags.
Media queries in CSS cater to specific device conditions—viewport width, orientation. This ensured fluidity across screens and resolutions.
Tools for Testing and Implementing Responsive Design
Testing is non-negotiable. Browsers like Chrome and Firefox come with built-in developer tools for responsive testing.
Services like BrowserStack let you test on countless devices and browsers.
Explore Lighthouse for performance metrics and improve efficiency. Responsive design frameworks like Bootstrap and Foundation offer a head start.
Soft Skills for Web Designers
Communication Skills
Importance of Clear Communication with Clients and Team Members
Clear communication isn’t a buzzword—it’s the lifeline. Misunderstandings can derail projects faster than a bug in your code.
With clients, it means understanding their vision and translating it into pixels. With team members, it ensures coherence, reducing friction.
Communication is the thread that weaves creativity and pragmatism together.
Techniques for Effective Communication
It’s not just what you say, but how you say it. Active listening—hear them out, then reiterate to confirm.
Clarity is key in emails; avoid jargon, be concise. Regular updates via meetings or reports. Share visual mockups to convey ideas, not just words. Use storytelling. Make the mundane captivating.
Tools to Enhance Communication
The right tools transform communication. Slack for instant messaging, threading conversations.
Trello for visual project management. Video calls through Zoom—face-to-face, even miles apart.
Google Docs or Confluence for collaborative documentation. Different tools, one goal—seamless flow.
Time Management
Strategies for Managing Time Effectively
Time slips away faster than you can hit refresh. Prioritize tasks—urgent vs. important. Break down projects into digestible chunks.
Use Pomodoro Technique—focus intensely, break briefly. Delegate when needed. Adapt and stay agile.
Tools for Scheduling and Tracking Progress
Digital allies abound. Google Calendar for events, sync across devices. Asana or Monday.com for project tracking.
RescueTime to audit where hours go. Integrate them—one cohesive system. Toggl for time tracking, see the minutes tick away.
Balancing Multiple Projects
The balancing act—master it. Juggling several projects means keeping balls in the air. Define boundaries—allocate time slots, stick to them.
Regular status checks. Flexibility to pivot when priorities shift. Never letting one project overshadow another.
Problem-Solving
Common Challenges in Web Design
Roadblocks, oh they come in myriad forms. Browser compatibility issues or site not rendering as expected.
Client feedback loop feels endless. Load times too slow, or the CMS doesn’t cooperate. Challenges aren’t exceptions; they’re constants.
Approaches to Effective Problem-Solving
Identify, isolate, ideate. Break the problem into smaller parts. Root cause analysis—ask “why” till you hit the core.
Leverage your network, get second opinions. Prototyping to test solutions quickly. Document the solution; future-you will thank you.
Critical Thinking
Analyzing User Needs and Website Performance
Analytics aren’t just numbers. They narrate user behaviors. Track through Google Analytics or Hotjar.
Heatmaps reveal where eyes linger. Surveys for direct user feedback. Data paired with intuition—analyzing needs becomes second nature.
Creative Solutions for Design Challenges
Constraints often breed creativity. Client demands something revolutionary—think outside the box. Implement unconventional layouts using CSS Grid.
Use SVG animations for engaging visuals. Don’t just solve problems; innovate within parameters.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Iteration is perfection. Post-launch isn’t the end; it’s a phase. Gather feedback. A/B test variations. Weekly sprints for minor tweaks.
Agile methodology keeps improvements rolling. Never settle; always evolve.
Additional Skills and Knowledge
Online Marketing
Role of Online Marketing in Web Design
Collapsed under the sheer weight of stunning visuals? Pause. Imagine; they just sit there. Online marketing steps in, breathing life.
Elevating from static to dynamic, marketing bridges the gap between design and audience. It drives traffic, engagement, conversions. Clarity meets strategy—a symbiotic dance.
Techniques: SEO, Social Media Marketing, PPC
SEO—your site’s behind-the-scenes hero. Keyword strategizing, backlinking. A jigsaw puzzle of content and performance.
Social media marketing, the buzzing hive. Curating visuals, crafting narratives. Platforms like Instagram, Twitter, Facebook—they aren’t extracurricular, but core.
And then PPC—precision shots. Google AdWords or Facebook Ads. Money where your mouse is.
Integrating Marketing Strategies with Web Design
Seamless. That’s the keyword. Your design should weave these strategies like threads in a tapestry. SEO? Fast load times, clean code, alt texts.
Social media integration—buttons within reach, shareable moments. PPC landing pages—direct, uncompromising. It’s the ultimate blend, a cocktail of design and intent.
Design Applications and Tools
Overview of Essential Design Tools (Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, Figma)
Adobe Photoshop—your Swiss Army knife. Pixel perfection, photo manipulations.
Then there’s Adobe Illustrator—vector graphics, logos, icons. Scalability without a hitch.
Enter Figma. Collaborative. Intuitive. Real-time design—you and your team, making magic.
Best Practices for Using Design Software
Master your toolset. Layers in Photoshop—keep them organized, name them like your sanity depends on it.
In Illustrator, leverage pathfinder, master the pen tool. In Figma, components and auto-layouts—game changers.
Shortcuts. They aren’t cheats. They’re efficiency incarnate.
Tips for Creating High-Quality Designs
Every pixel matters. Grid systems, aligning principles. Consistency doesn’t breed boredom; it breeds coherence. Play with whitespace—negative space isn’t void; it’s valiant.
Contrast, balance, emphasis. These aren’t optional—they’re the lifelines. Know the rules like a pro so you can break them like an artist.
Project Management
Setting Project Goals and Milestones
Without a map, you’re lost before you begin. SMART goals—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound. Milestones break mammoths into manageable bites.
Vision meets execution.
Tracking Progress and Managing Resources
Data-driven decisions. Kanban boards, Gantt charts, burndown charts. Track not just time but energy and mana. Juggle resources—human, technological.
Tools for Effective Project Management
Trello. Buckets and cards, shifting sands.
Asana. Lists, timelines, dependencies.
Jira. For when you’re knee-deep in agile sprints.
Practical Tips for Skill Development
Pursuing Education and Certifications
Formal Education vs. Self-Learning
Ah, the age-old debate. Formal education grants structure, a guided path. Degrees offer credibility. But then, self-learning—it’s the wild, untamed forest of discovery. No syllabus, just raw curiosity. Both paths hold merit.
Formal education: universities, boot camps.
Self-learning: YouTube, blogs, trial and error.
Balance, perhaps? Mix the discipline of formal with the freedom of self-learning. Craft your journey.
Industry-Recognized Certifications
Certifications, the badges of honor. They speak volumes. Adobe Certified Expert, Google Analytics, HubSpot’s Inbound Certification. They aren’t just paper—they’re proof.
Prove your mettle.
Focus on certifications that align with your goals. They open doors.
Online Courses and Resources
The internet—an endless tome of knowledge. Coursera, Udemy, LinkedIn Learning. Classes at your pace, on-demand. Interactive, engaging platforms.
Explore Khan Academy for basics, move to edX for advanced topics.
Forums like Stack Overflow—where queries meet solutions. Codecademy and Treehouse for coding conquests.
Gaining Experience
Building a Professional Portfolio
A portfolio speaks louder than resumes. Craft a digital showcase. Dribbble, Behance, your personal site.
Design samples, case studies, before-and-after scenarios. It’s not just what you did, but how you did it.
Diverse projects. Web design isn’t a one-trick pony. Show versatility.
Internships and Freelance Opportunities
Real-world experience—gold. Internships, the gateway to industry nuances.
Freelancing, a step further. Platforms like Upwork, Fiverr. Small gigs turning into a blooming career. You learn to navigate clientele, budgets, scopes. It’s hands-on web designer skills, no theory, all practice.
Learning from Industry Experts
Mentorship, an underrated gem. Follow industry legends—A List Apart, Smashing Magazine.
Podcasts, design webinars. Engage, participate in Q&As. Twitter threads, LinkedIn posts. Insights distilled from years of expertise.
Keeping Up with Trends
Importance of Staying Updated with Industry Trends
Web design—it evolves. Blink and you miss the shift. Trends aren’t fluff; they dictate user expectations. Parallax scrolling, minimalism, immersive 3D elements. Staying updated isn’t optional; it’s survival.
Resources for Continuous Learning
Blogs—CSS-Tricks, SitePoint, Designmodo.
Online magazines, webinars. Medium, packed with firsthand stories, tips. Podcasts, youtube channels. Subscribe, read, watch.
Participating in Web Design Communities
Be part of the hive. Reddit, Designer Hangout, The Designer’s League.
Meetups, conferences. Physically, virtually. Contribution is key. Share your work, get critiques, improve.
Collective wisdom, personal growth.
FAQ On Web Designer Skills
What are the essential skills for a web designer?
A web designer needs proficiency in HTML/CSS for layout and styling. Adobe Creative Suite is crucial for graphic design, while JavaScript basics enhance interactivity.
Mastering responsive design, typography, and understanding user-centered design principles can take your skills up a notch, alongside CMS platforms like WordPress.
How important is responsive design in web design?
Responsive design is vital. Adjusting layouts for various screen sizes ensures optimal user experience. Skills in cross-browser compatibility, using frameworks like Bootstrap, and understanding digital design trends are crucial.
Google prioritizes mobile-friendly sites, affecting your SEO and visibility.
What are the best tools for web designers?
Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Illustrator, and Figma are top-tier graphic design tools. For coding, editors like Visual Studio Code excel. GitHub aids in version control, while platforms like Sketch streamline wireframing and prototyping.
Using these tools enhances your visual design precision and flexibility.
How does SEO relate to web design?
SEO fundamentals are critical to ensure your work gets seen. Implementing SEO improves page load speed, multimedia integration, and content strategy.
Google Analytics helps track user behavior. Structuring your content well and optimizing images contribute to higher conversion rates and better search rankings.
What is the role of UX/UI design in web design?
UX/UI design is the backbone of a functional website. User experience focuses on usability and satisfaction, while user interface design optimizes the visual aspects.
Wireframing, prototyping, and doing usability testing inform better design decisions. Ensuring web accessibility makes your designs inclusive and effective.
How does typography impact web design?
Typography significantly affects readability and aesthetics. Knowledge in typography helps create engaging website layouts.
Balancing branding guidelines and design principles, choosing the right font styles, sizes, and line heights can drastically improve user interaction and the overall look and feel of a site.
Why is understanding web accessibility important?
Web accessibility ensures your site is usable by everyone, including those with disabilities. Adhering to Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) ensures compliance.
Accessible sites improve overall UX/UI and widen your audience reach. Inclusive design is a must in today’s diverse digital landscape.
How do wireframing and prototyping streamline the design process?
Wireframing and prototyping are essential in visualizing and testing your design concepts. Tools like Figma and Sketch facilitate this process.
They allow you to pinpoint interactive design elements and information architecture before full-scale development, saving time and avoiding costly revisions.
What is the significance of web performance?
Web performance impacts user retention and SEO. Optimizing for page load speed and efficient coding standards using JavaScript and CSS is crucial.
Techniques like using SASS for better stylesheet management and compressing images can significantly enhance performance, ensuring a smoother user experience.
How does one stay current with web design trends?
The field is dynamic; staying up-to-date is critical. Follow digital design trends, engage with the web design community, and constantly experiment with new tools and frameworks.
Continuous learning in multimedia integration, leveraging GitHub repositories, and attending industry webinars ensure you remain ahead.
Conclusion
Embracing web designer skills is your gateway to turning visions into digital reality. Mastering the core elements—from HTML/CSS to responsive design—is non-negotiable. Incorporate SEO fundamentals to boost visibility, ensuring your designs reach wider audiences.
Delve into the intricacies of UX/UI design and employ tools like Figma and Adobe Creative Suite to prototype and perfect. Prioritize web accessibility to make your designs inclusive, adhering to WCAG.
Typography and color theory will elevate your aesthetic game, while cross-browser compatibility and page load speed enhancements refine functionality. Embrace continual learning: follow digital design trends and leverage GitHub for collaborative efficiency.
Ultimately, becoming proficient in web designer skills means harmonizing creativity and technical know-how. Your ability to create user-centered, visually stunning, and high-performing websites will set you apart. Let these skills transform your projects into captivating experiences. Ready to take your designs to the next level? Make every pixel count, every line of code purposeful.