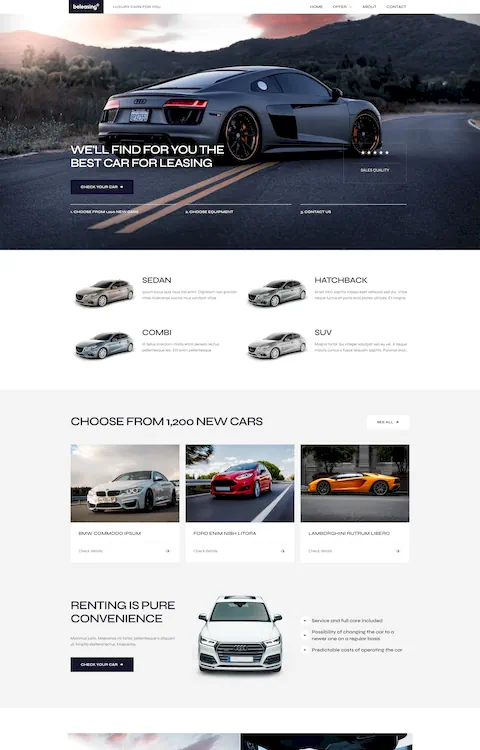
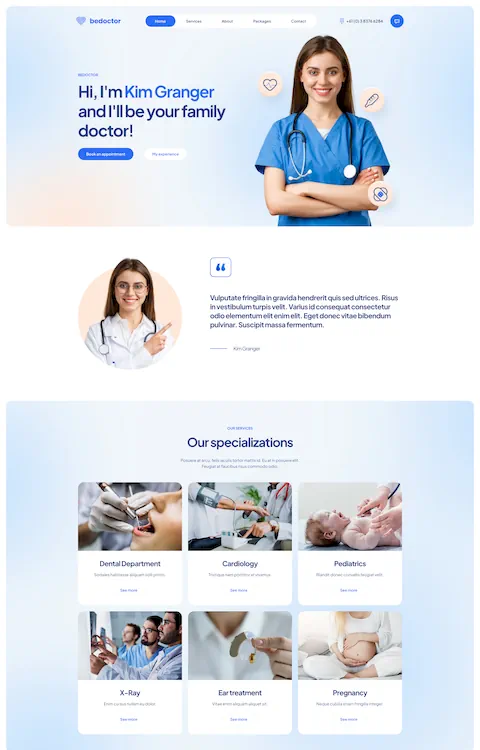
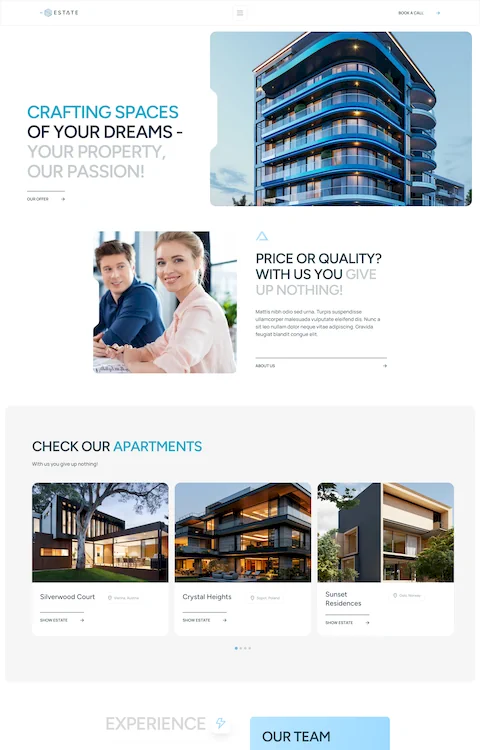
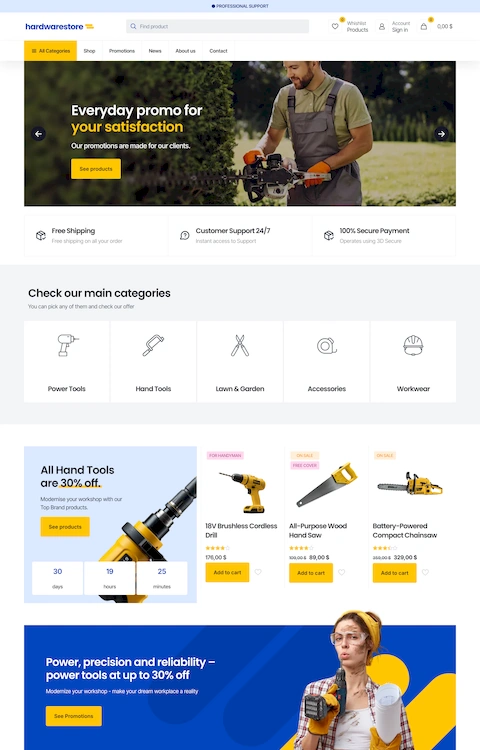
Awesome House Cleaning Website Design Examples
October 19, 2025
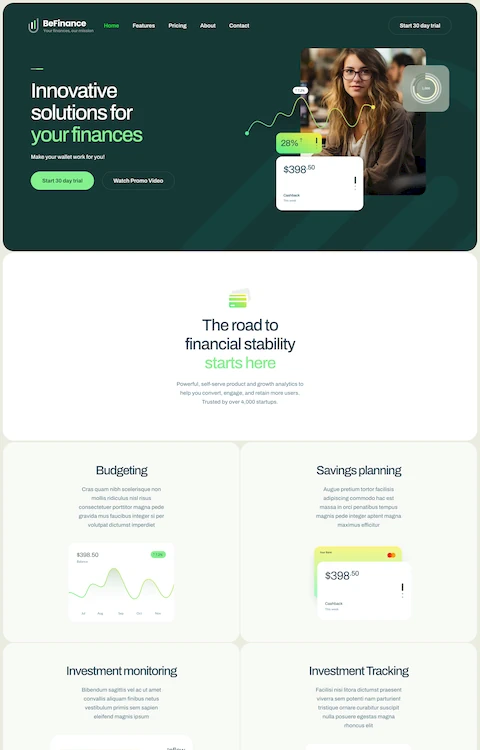
The Best Modern Examples of Finance Website Templates
October 21, 2025Scrolling used to be boring. Then parallax changed everything.
This layered scrolling technique creates depth perception by moving background and foreground elements at different speeds. The result? Flat pages transform into immersive browsing experiences that keep visitors engaged.
But not every implementation works. Some sites nail the balance between visual storytelling and performance. Others sacrifice user experience for flashy effects.
This collection of parallax scrolling website design examples shows what separates the good from the forgettable.
You'll find portfolio sites, product pages, creative agency homepages, and single-page layouts that actually convert. Plus technical breakdowns of CSS3 techniques, JavaScript libraries like GSAP ScrollTrigger, and accessibility guidelines you can't ignore.
What is Parallax Scrolling
Parallax scrolling is a web design technique where background images move slower than foreground elements during vertical scrolling.
This speed difference creates a 3D illusion effect, adding depth perception to otherwise flat web pages.
The technique originated in 2D video games during the 1980s. Developers used layered scrolling to simulate distance and movement in side-scrolling games like Super Mario Bros.
Ian Coyle brought parallax to web design in 2011 with the Nike Better World campaign. That single project changed how designers thought about scroll-based interactions.
Today, parallax appears everywhere. Product landing pages, portfolio sites, agency websites, and brand experiences all use this immersive browsing technique.
The effect works because it mimics how human eyes perceive depth in the real world. Distant objects appear to move slower than closer ones.
Epic Examples of Parallax Websites in Action
Clingr
Blockchain AI. ChainGPT
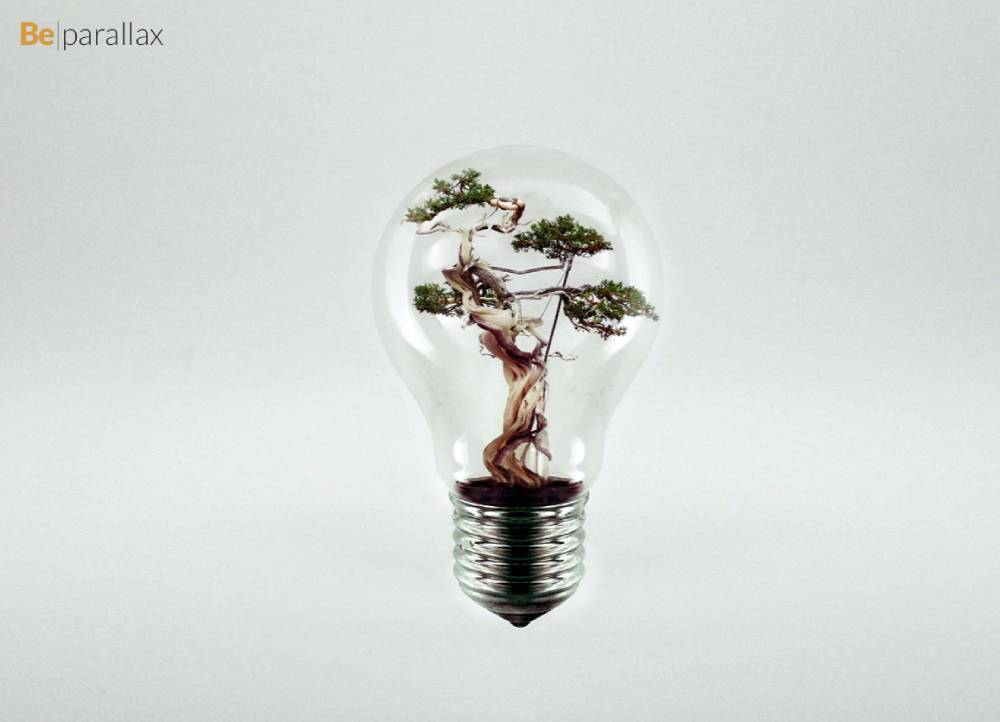
BeParallax
PORSCHEvolution
65dB
Dyvo AI
Get Some Fresh Air
ULTROM
Qode Interactive Catalogue
BeFestival2
GIANT 105
Landor & Fitch
Agence Norry
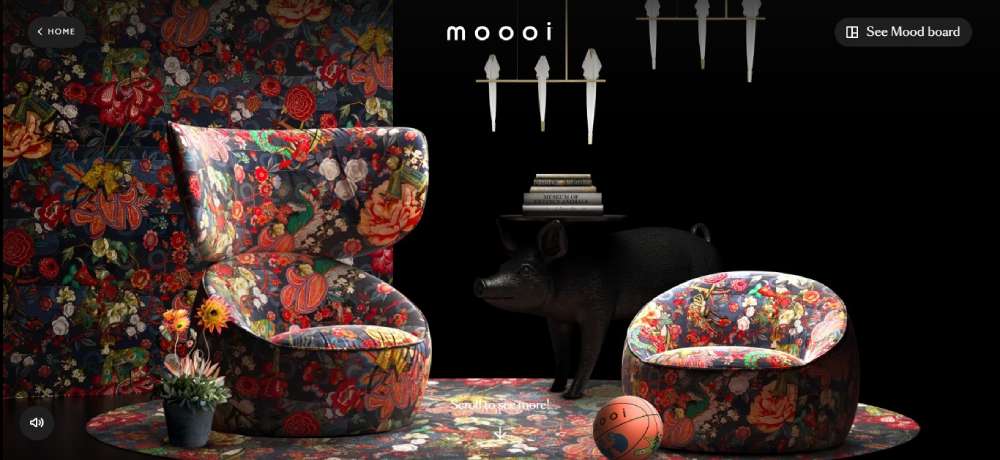
Mooi
OUTSTANDLY
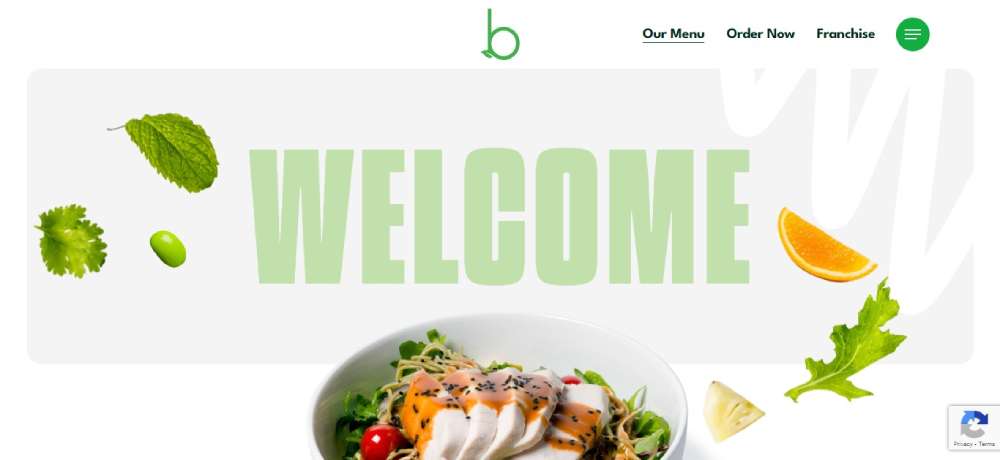
BeBistro4
Phyll
WHY COLLECT SEASHELLS
The story of The Goonies
GREAT INTERSECTION
Unfold
BeMarathon
Louie Sellers
CHRIS KALAFATIS - PORTFOLIO
Dogstudio
Eidsiva
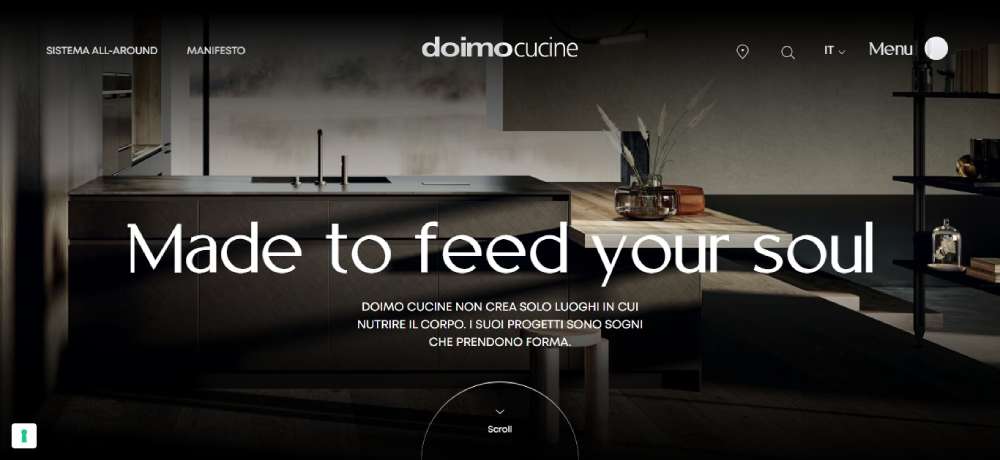
DOIMO CUCINE
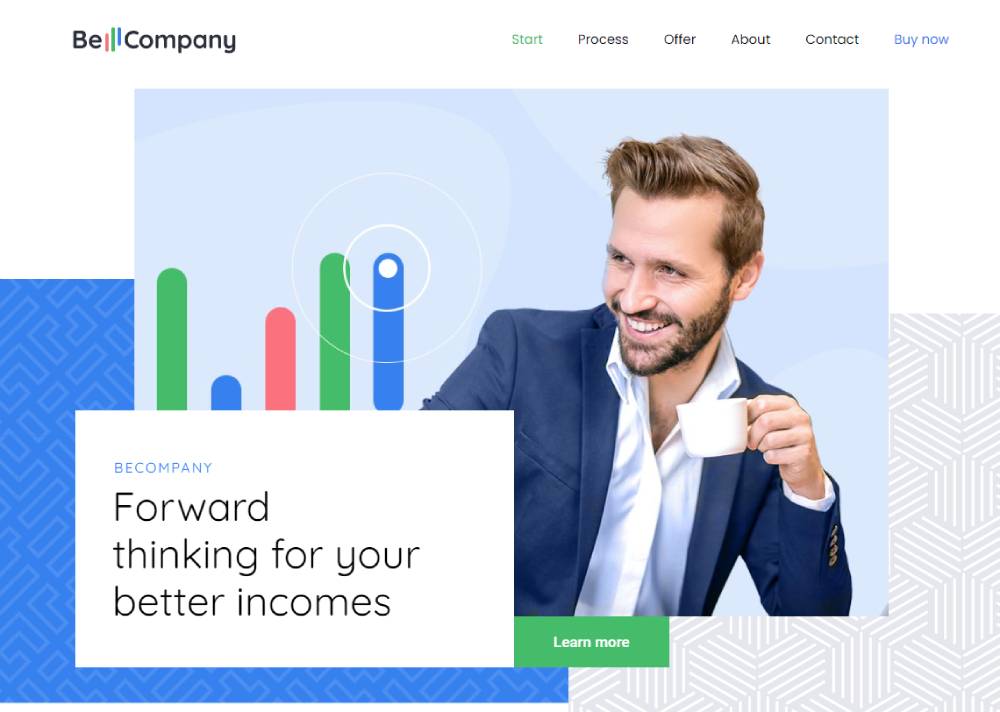
BeCompany4
Bagigia
New York Times: Tomato Can Blues
Verse
Rossini Caviar
ToyFight
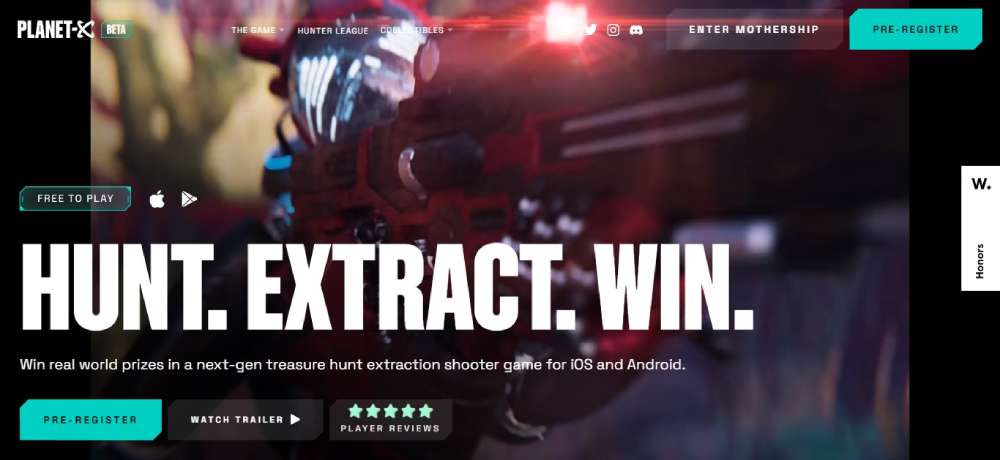
PLANET-X
Diesel: BAD Guide
Javier Sánchez
Dockyard Social
Evmos
Firewatch
LetZKola
Delassus Group
Alamance Foods
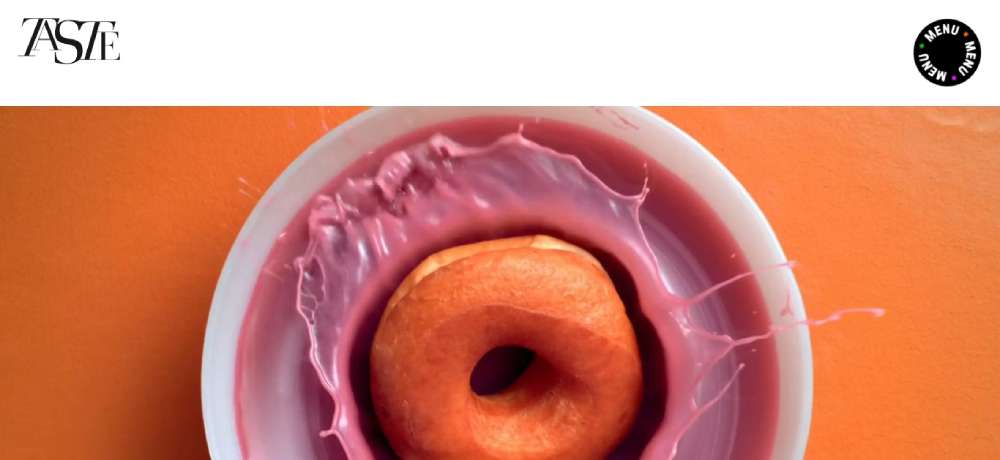
TASTE
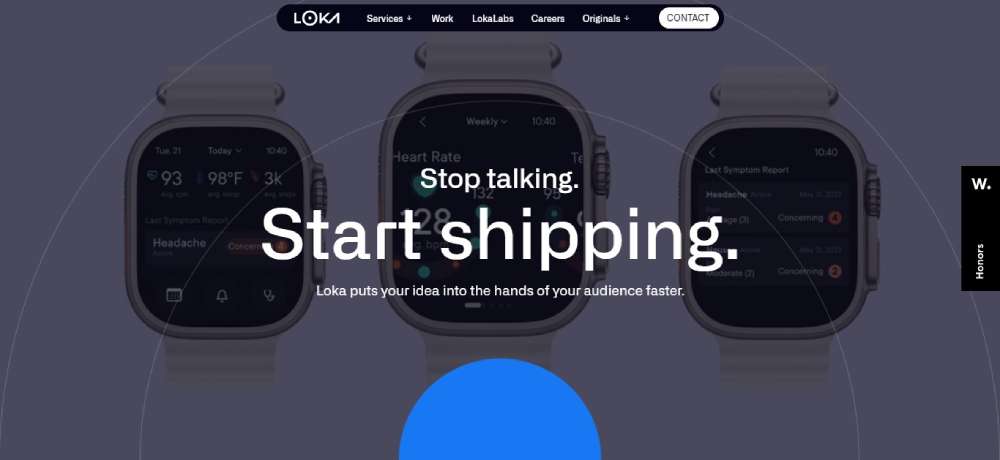
Loka
WWF
Tatort Ruhrpott
The Tech Playground
The Haircut
Matin
Kawi Crossfit
HARMONIOUS CADENCE OF SOUND
Okalpha
Noomo Agency
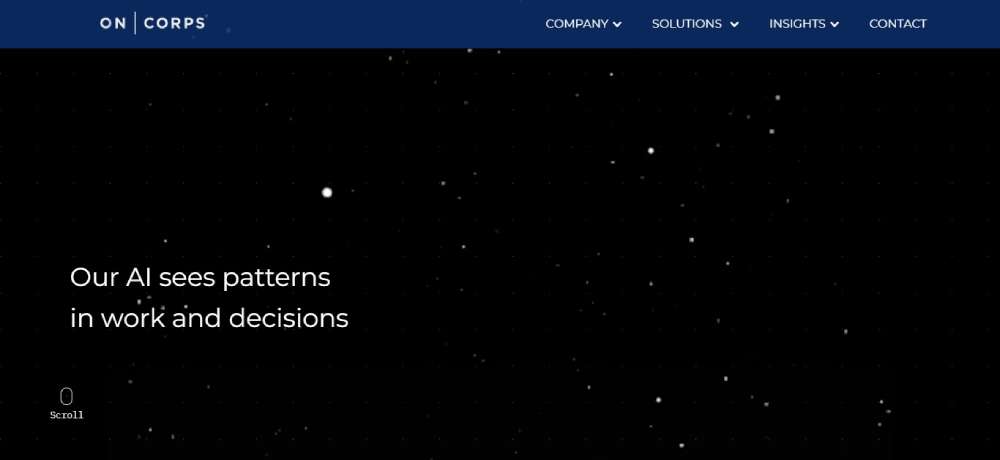
OnCorps AI
loOt
Unveil
Jomor Design
BANANA BLOSSOM SALADS
Avenir Creative
Openlands
AMPLIFIDOR
Zion Adventure Photog
Cielia Life Design Selection
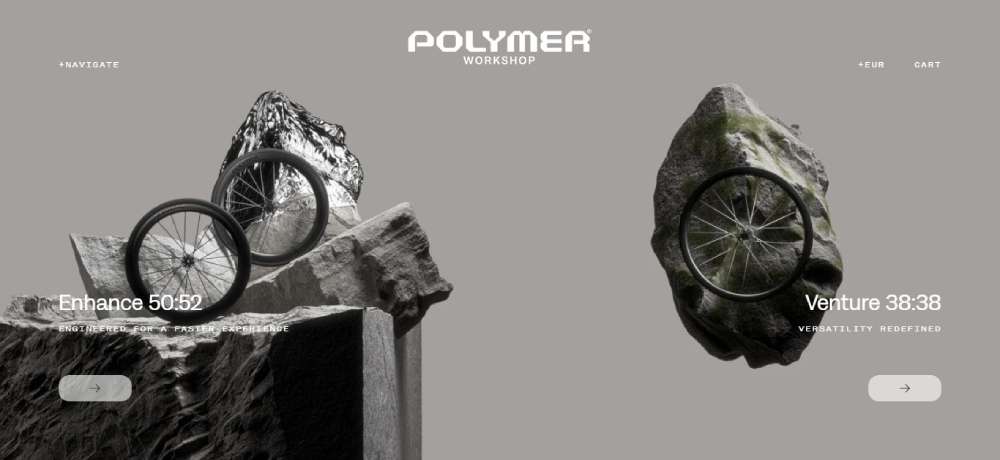
Polymer Workshop
Nixie
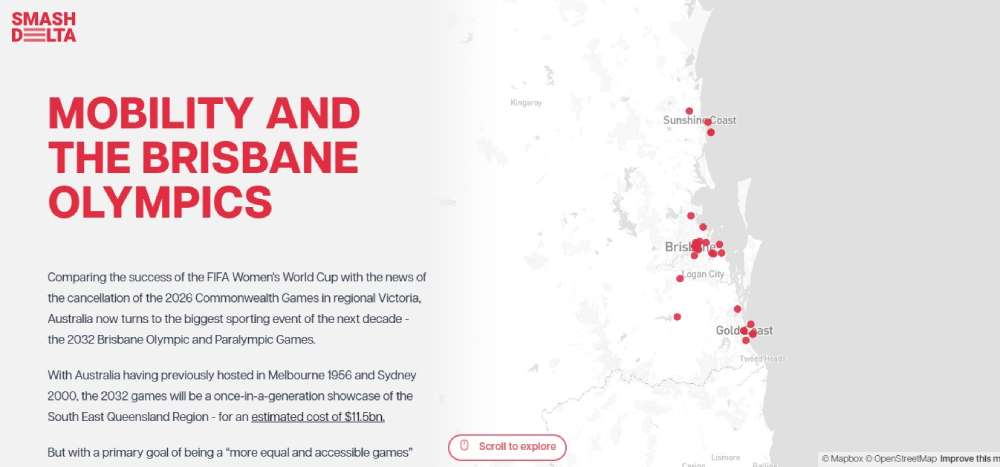
Brisbane Olympics
ONLY 8%
Zen Art
Content Lab
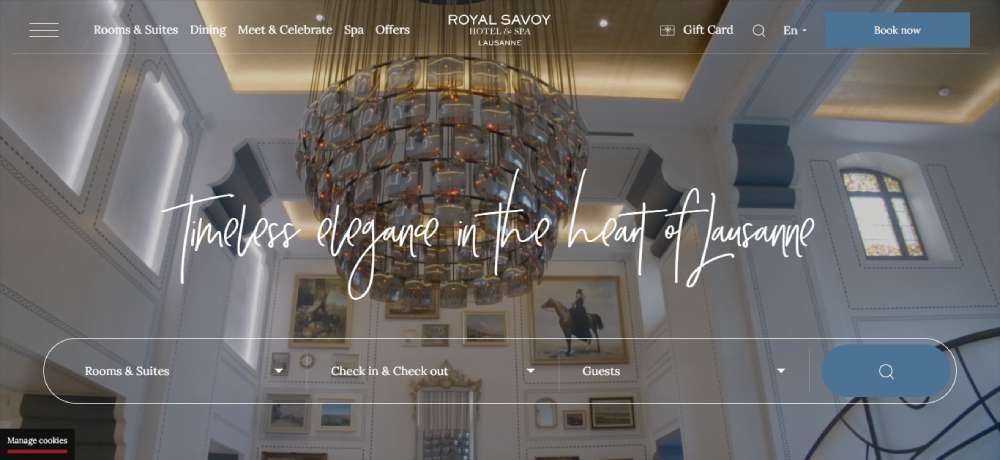
Royal Savoy Hotel & Spa Lausanne
CRONOS.NL
Carlos Alcaraz
SETAPRINT
LA CHAISE COUTURE
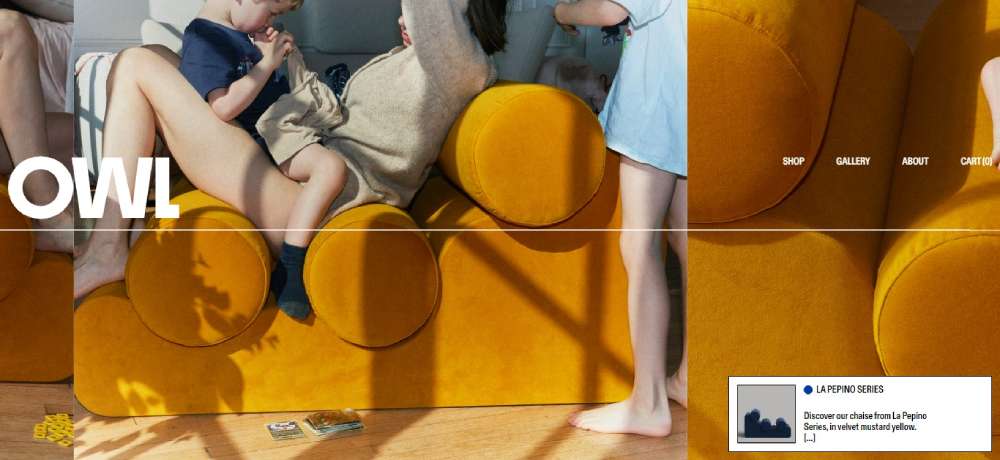
OWL
.Flaw
Amadeo
Visual Track
Margrete: Queen of the North
IDP
DHNN
LEN - PORTFOLIO TEMPLATE
How Parallax Scrolling Works
The core mechanic is simple: separate your page into multiple layers, then move each layer at different scroll velocities.
Background elements scroll slower. Foreground elements scroll faster. Your brain interprets this as perspective depth.
CSS Implementation
The quickest method uses background-attachment: fixed in CSS3. This keeps background images stationary while content scrolls over them.
For more control, use CSS transform translate effects combined with scroll position tracking.
JavaScript Libraries
Complex parallax requires JavaScript. GSAP's ScrollTrigger dominates professional implementations for scroll-triggered animations.
Locomotive Scroll offers smooth scrolling animation with minimal setup. Rellax.js handles lightweight projects. ScrollMagic works well for scene-based animations.
The Technical Process
Here's what happens during a parallax scroll:
- Browser detects scroll event through event listeners
- JavaScript calculates scroll percentage and viewport position
- Transform values update for each layer based on assigned scroll velocity
- Browser repaints affected elements using z-index layering
The Intersection Observer API helps trigger animations only when elements enter the viewport. This improves performance significantly.
Types of Parallax Effects in Web Design
Not all parallax behaves the same way. Different effect types serve different purposes.
Vertical Parallax Scrolling
The classic approach. Background moves up while you scroll down, creating depth as you navigate through sections.
Most one page website designs use this technique.
Horizontal Parallax Scrolling
Layers move left or right instead of up and down. Works well for timelines, product showcases, and interactive websites telling linear stories.
Mouse-Movement Parallax
Elements respond to cursor position rather than scroll. Subtle movements follow your mouse, creating a responsive feel without any scrolling required.
Parallax.js handles this effect specifically.
Layered Parallax (Multi-Depth)
Multiple layers move at different speeds simultaneously. Three, four, even ten layers can create rich depth perception.
The Firewatch game website demonstrates this perfectly with its forest landscape built from numerous overlapping layers.
Scroll-Triggered Parallax Animations
Elements animate based on scroll position rather than continuous movement. Images fade in, text slides up, objects rotate as you reach specific scroll points.
This type pairs well with animated websites and animated landing page designs.
How to Create Parallax Scrolling on Your Website
Three paths exist: pure CSS for basic effects, JavaScript libraries for complex animations, or website builders for no-code implementation.
Your choice depends on technical skill and how much control you need over scroll velocity and layer behavior.
CSS and HTML Techniques for Parallax
The simplest CSS parallax uses background-attachment: fixed combined with background-size: cover. Background stays stationary while content scrolls over it.
For layered effects, use CSS3 transforms with perspective and translateZ properties:
perspective: 1pxon the container creates the 3D spacetranslateZ(-1px)pushes elements backward, making them scroll slowerscale()compensates for the size reduction from perspective
Pure CSS parallax works without JavaScript but offers limited control over timing and scroll percentage calculations.
JavaScript Libraries for Parallax Effects
GSAP ScrollTrigger dominates professional front-end development. Pin elements, scrub animations based on scroll position, create timeline-based sequences.
Locomotive Scroll provides smooth scroll behavior with built-in parallax. Single initialization handles both smooth scrolling and depth effects.
Rellax.js weighs under 1KB. Add data attributes to elements, set speed values, done. Perfect for lightweight projects.
ScrollMagic excels at scene-based animations where specific scroll positions trigger specific events.
Simple Parallax handles basic needs without the overhead of larger frameworks.
Website Builders with Built-in Parallax
Webflow leads for visual parallax implementation. Set scroll-based animations without touching code through its interactions panel.
WordPress with Elementor or Divi Builder includes parallax modules. Enable the effect with a toggle, adjust speed with a slider.
Wix offers parallax in its editor under strip backgrounds. Limited customization but zero learning curve.
Squarespace includes parallax options in certain templates. Check template features before committing.
Website builders sacrifice fine control for speed. Complex multi-layer effects still require custom code or dedicated web design tools.
Performance Considerations for Parallax Websites
Parallax kills page speed when implemented poorly. Multiple high-resolution background images plus continuous JavaScript calculations drain performance fast.
Core Web Vitals suffer most. Largest Contentful Paint delays when heavy images load. Cumulative Layout Shift spikes when elements reposition during scroll.
Image Optimization
- Compress all parallax images, target under 200KB per asset
- Use WebP format with JPEG fallbacks
- Implement lazy loading for below-fold parallax sections
- Consider CSS gradients instead of image backgrounds where possible
JavaScript Performance
- Throttle scroll event listeners to reduce calculation frequency
- Use
requestAnimationFrameinstead of direct scroll events - Implement Intersection Observer API to animate only visible elements
- Remove parallax effects entirely below 768px viewport width
Test with Google PageSpeed Insights and Chrome DevTools Performance panel. Aim for 90+ scores on both mobile and desktop.
Accessibility Guidelines for Parallax Scrolling
Motion affects people with vestibular disorders. The depth illusion and continuous movement cause dizziness, nausea, disorientation.
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) address this directly.
Required Accommodations
- Respect
prefers-reduced-motionmedia query, disable parallax when system setting is enabled - Provide toggle button letting users turn effects on/off
- Keep parallax subtle, avoid full-screen motion that dominates the viewport
- Limit effect duration and intensity
Implementation Check
Add this CSS to respect user preferences:
@media (prefers-reduced-motion: reduce) { .parallax { background-attachment: scroll; } }
Building accessible websites means giving users control over their experience. Parallax should enhance, never exclude.
Mobile Responsiveness and Parallax Design
Most parallax effects break on mobile. Touch scrolling behaves differently than mouse scrolling, and background-attachment: fixed fails on iOS Safari entirely.
Mobile-First Approach
Design without parallax first using mobile first design principles. Add effects progressively for larger screens.
Use media queries to disable complex animations below tablet breakpoints:
- 768px and below: static backgrounds only
- 769px to 1024px: simplified single-layer parallax
- 1025px and above: full multi-layer effects
Touch Device Considerations
Replace scroll-based parallax with mouse-movement parallax on touch devices. Or remove it completely.
Test on actual phones, not just browser emulators. The scroll momentum on iOS creates unpredictable behavior that Chrome DevTools cannot simulate.
Responsive websites adapt to device capabilities. Forcing desktop effects onto mobile creates frustration, not immersion.
Common Mistakes in Parallax Website Design
Seeing these errors repeatedly. Each one damages user experience, engagement metrics, or both.
Performance Disasters
- Uncompressed 5MB background images
- Parallax on every section instead of strategic placement
- No lazy loading for off-screen assets
- Ignoring mobile performance entirely
Design Failures
- Parallax that competes with content instead of supporting it
- Scroll velocity so fast it causes motion sickness
- Z-index layering that obscures text or call to action buttons
- Effects that distract from website navigation
Technical Oversights
- No fallback for browsers that don't support certain CSS properties
- Forgetting to test cross-browser compatibility
- Ignoring
prefers-reduced-motionaccessibility requirements - Using deprecated JavaScript libraries
Strategic Errors
- Adding parallax because it looks cool rather than serving a purpose
- Prioritizing visual effects over page load speed
- Copying complex implementations without understanding the code
- No measurement of how parallax affects bounce rate or time on page
The best parallax sites use the effect sparingly. One or two well-executed sections beat ten mediocre ones.
Review sites with good UX for reference. Notice how restraint and purpose guide their animation choices.
Check your work against bad design examples too. Learning what fails teaches as much as studying success.
FAQ on Parallax Scrolling Website Design
What is parallax scrolling in web design?
Parallax scrolling is a technique where background images move slower than foreground elements during vertical scrolling. This speed difference creates a 3D illusion effect and depth perception, making flat web pages feel more immersive and engaging.
Does parallax scrolling affect SEO rankings?
Not directly. Search engines care about page load speed and mobile responsiveness more than the scroll effect itself. Heavy JavaScript libraries that slow loading times hurt rankings, but lightweight CSS3 implementations rarely cause problems with Core Web Vitals.
Which JavaScript libraries work best for parallax effects?
GSAP ScrollTrigger dominates professional implementations. Locomotive Scroll offers smooth scrolling with minimal setup. Rellax.js handles lightweight projects under 1KB. ScrollMagic excels at scene-based scroll-triggered animations.
Can I create parallax without coding?
Yes. Webflow builds parallax interactions visually through its interactions panel. WordPress with Elementor includes parallax modules. Wix and Squarespace offer built-in parallax options in certain templates with simple toggle controls.
Does parallax work on mobile devices?
Poorly in most cases. Touch scrolling behaves differently than mouse scrolling, and background-attachment: fixed fails on iOS Safari. Best practice is disabling complex parallax effects below 768px viewport width.
How do I make parallax accessible?
Respect the prefers-reduced-motion media query to disable effects when users request it. Provide a toggle button for manual control. Keep movements subtle and avoid full-screen motion that dominates the viewport. Follow WCAG guidelines.
What types of websites use parallax best?
Portfolio sites, creative landing pages, product showcases, and visual storytelling projects benefit most. The effect works well when immersive browsing experience matters more than dense information delivery.
How many parallax sections should a page have?
One or two well-executed sections beat ten mediocre ones. Overusing parallax creates performance issues and visual fatigue. Strategic placement at key moments, like the hero section or product reveals, delivers the strongest impact.
What are common parallax implementation mistakes?
Uncompressed large images, parallax on every section, ignoring mobile performance, no accessibility fallbacks, and effects that compete with content instead of supporting it. Testing with Google PageSpeed Insights catches most issues.
Which sites have the best parallax scrolling examples?
Apple product pages set the standard. Firewatch demonstrates multi-layer depth. The Boat redefined interactive storytelling. PORSCHEvolution showcases timeline-based scrolling. Awwwards and Dribbble feature curated collections of award-winning parallax implementations.
Conclusion
These parallax scrolling website design examples prove one thing: motion matters when it serves a purpose.
The best implementations guide attention through scroll-based interactions without sacrificing page speed or accessibility. They use GSAP ScrollTrigger, Locomotive Scroll, or pure CSS3 transforms strategically, not everywhere.
Start with mobile responsiveness as your baseline. Test scroll velocity on actual devices. Watch your Core Web Vitals metrics closely.
Remember the prefers-reduced-motion` query. Some visitors need parallax disabled entirely.
Whether you're building a web design portfolio, launching startup landing pages, or refreshing corporate websites, the principle stays constant.
Restraint beats excess. One memorable scroll-triggered animation creates more impact than ten forgettable ones.
Now go build something worth scrolling through.